Mechanical plastics, otherwise known as engineering plastics, refers to plastics that are used in applications due to their mechanical nature or functionality, rather than their appearance. Many mechanical plastics can be substituted for metal parts, which results in a cost savings and lower material weights without sacrificing material durability.
Strength and Resilience
Mechanical plastics offer superior strength and resilience compared to other types of commodity plastic materials. There is a broad range of mechanical plastics with varying characteristics. While most are lightweight, some can be heavy. There are varying degrees of thermoplasticity and machinability. There also are various degrees of resistance to high-impact situations, heat resistance, and chemical corrosion resistance.
Most are considered environmentally friendly since they can be recycled; however, this does not apply to all engineered plastic varieties or types. Industry applications will vary depending upon the type of engineering plastic, but can include automotive, manufacturing, electronics, transportation, food processing, medical, and more. See our “Mechanical Properties of Common Plastic Sheets” graph below to see how different mechanical plastics compare for different attributes.
Common mechanical plastics include: Nylon, Acetal, Tefzel (ETFE), Ultem (PEI), Sintra (PVC), ABS, PTFE, UHMW, PVDF, PEEK, HDPE
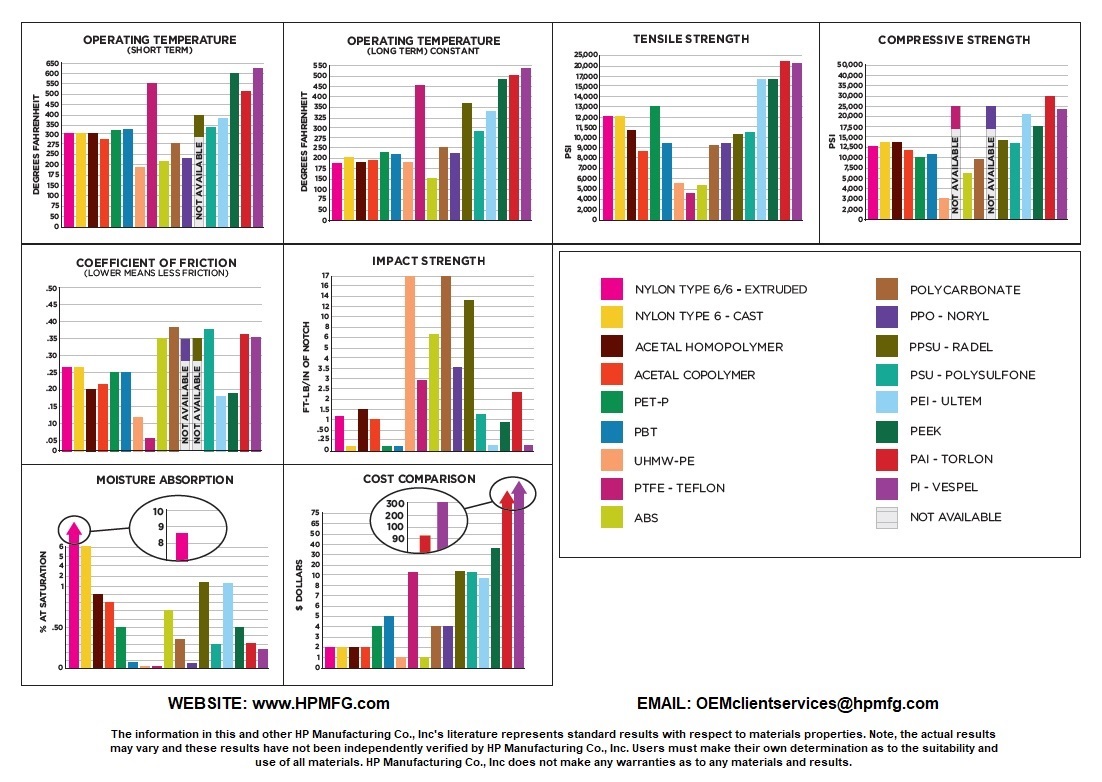
The below shows key characteristics for various thermoplastics in relation to cost, thermal stability and chemical resistance.
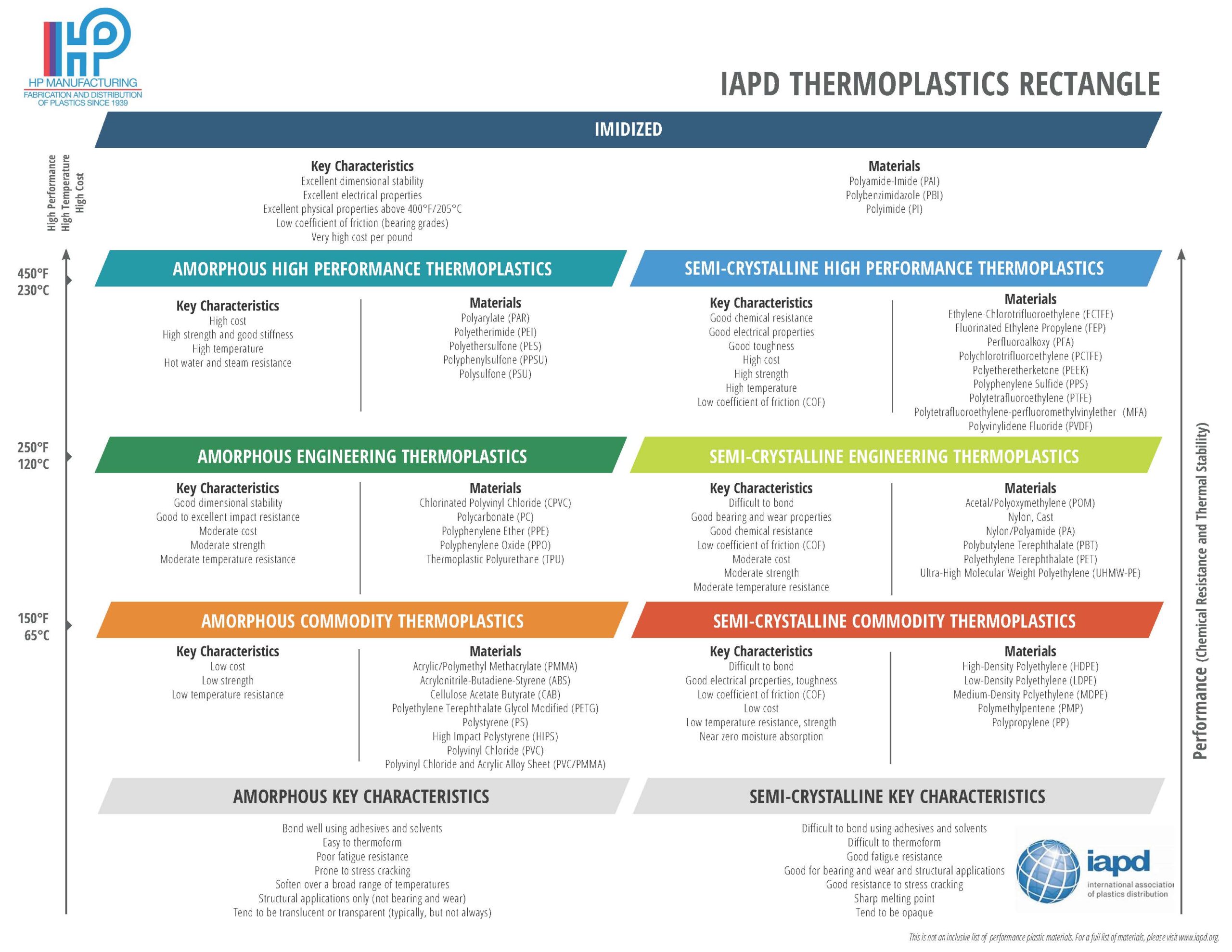
Learn more about each of these engineering plastics on our blog.









