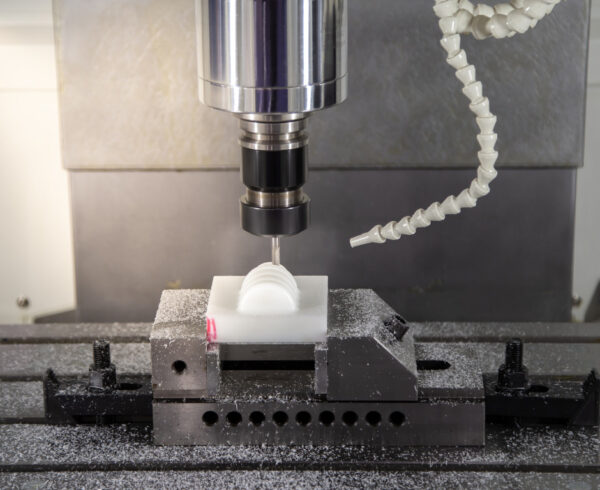
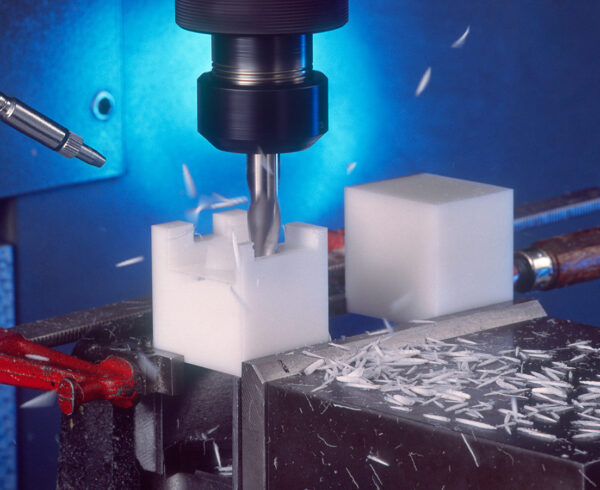
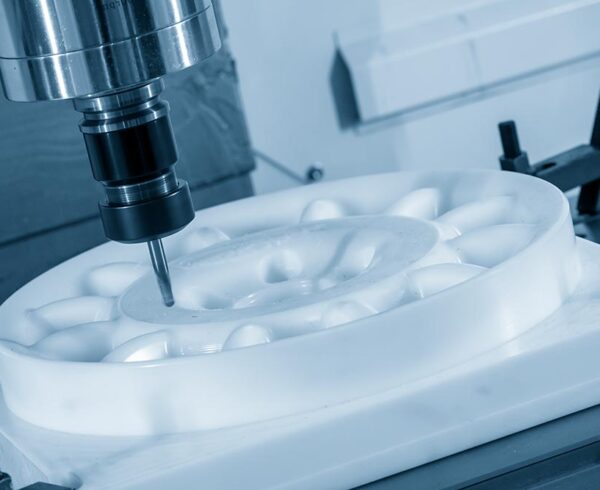
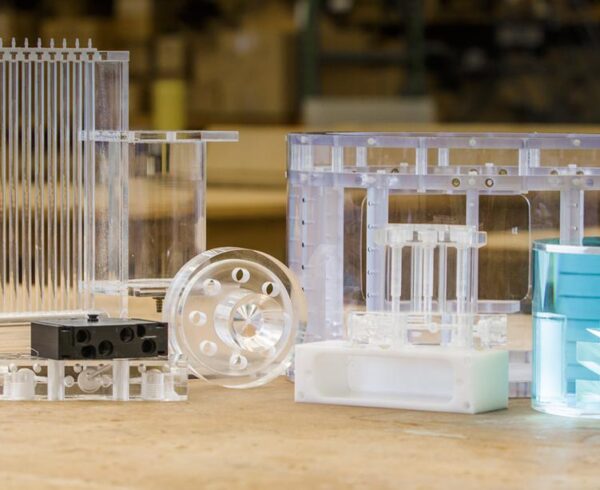
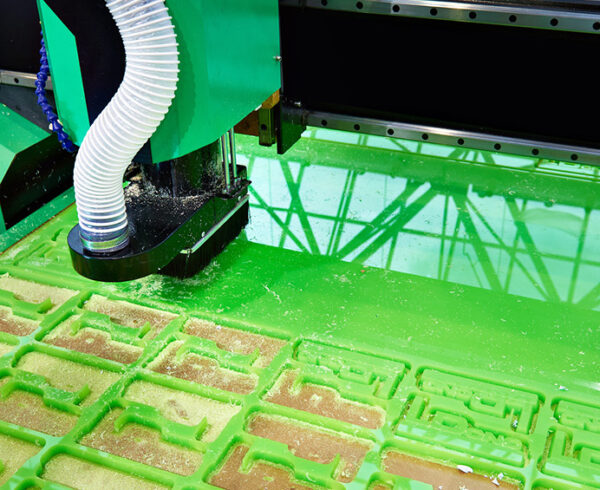
Any OEM looking for custom, quality plastic components manufactured to tight tolerances inevitably looks to CNC machining. It not only offers the quality needed, but its fast start-up time (no molds are required) makes it the go-to choice for many design engineers.
Because plastic fabrication is used in a variety of industries, including industrial and heavy equipment, medical, electronics and aerospace, engineers need to understand the materials and special requirements most commonly seen in each sector to make informed design decisions to best leverage plastic fabrication technology for their projects.
Plastic Fabrication in Industrial Applications
 CNC machining offers the widest variety of materials options, which makes it the premier choice for industrial applications. Machinery and heavy equipment manufacturers use plastics for a diverse range of components, including wear pads, protective guarding, gears, housings, valves, spacers, cable management, and more. These parts often require high-stress, high-load, high-temperature, or chemical resistance.
CNC machining offers the widest variety of materials options, which makes it the premier choice for industrial applications. Machinery and heavy equipment manufacturers use plastics for a diverse range of components, including wear pads, protective guarding, gears, housings, valves, spacers, cable management, and more. These parts often require high-stress, high-load, high-temperature, or chemical resistance.
Some of the most popular materials for industrial plastic fabrication include:
- Polycarbonate (PC) – PC is a durable plastic that can withstand environments and high temperatures. Polycarbonate has great clarity.
- Nylons – These polyamide materials are among the most common plastics used in industrial applications due to their strength and durability. Nylon is a relatively inexpensive material that is easily machined to extremely tight tolerances.
- Delrin® – This acetal homopolymer is often used to replace metal due to its density, stiffness, and tensile strength. This impact-resistant material is ideal for applications where the part is moving or exposed to moisture and chemicals.
- TIVAR® 88 – TIVAR polyethylene is ideal for applications requiring corrosion, moisture, and wear resistance at temperatures up to 175 degrees F.
- UHMW – Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene features excellent abrasion and impact resistance, as well as noise reduction. Being chemically inert, UHMW is ideal for industrial food contact applications.
Plastic Fabrication in the Medical Industry
Plastics have become an integral part of the healthcare industry for everything from single-use disposables to implants to the equipment used to diagnose illnesses. OEMs of Class II and III medical devices face strict regulatory requirements in the design and manufacture of their products. The components used in these devices may require the plastic to be safe for human contact, antimicrobial, compatible with repeated sterilization, and able to support complex geometries.
One of the most important factors for fabricated medical plastics is ensuring your supplier can machine and assemble these devices with extremely tight tolerances and repeatable quality. Fabricators also need to provide you with certified materials, serialization, BOM management, full traceability, and Certificates of Conformance. REACH and RoHS compliance may also be required.
Materials commonly used in medical fabrications include:
- Acrylic/Plexiglas® – Scientifically known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), acrylic is favored for its crystal clarity, shatter resistance, light weight, cleanability, and machinability. PMMA is used in diagnostic imaging phantoms, in fluoroscopic pediatric cradles, and in other immobilization braces used in medical imaging.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) – PEEK is ideal for medical devices due to its mechanical strength and elasticity. PEEK also is resilient to radiation, high temperatures, abrasion, and wear.
- Polycarbonate (PC) – One of the most versatile plastics for fabrication, polycarbonate material is autoclavable, impact-resistant, and offers superior clarity for medical applications. PC can be found in surgical instruments, connectors, centrifuge bowls, and more.
Custom Fabrication for Electrical and Electronic Devices
Plastics are the go-to choice for electronic components due to their non-conductive, static-dissipative, and nonflammable options. Many plastics can withstand high voltages and temperatures without material degradation, and their corrosion- and water-resistance increase product safety and reliability. Plus, the machinability of plastics enables virtually unlimited options in complex electrical designs.
Materials often used in electrical and electronic assemblies include:
- GPO-3 – This glass-reinforced polyester is a durable, impact-resistant plastic with outstanding flame, arc, and track resistance. GPO-3 is used to make electrical insulators, terminal blocks, and strain reliefs.
- Acrylonite Butadiene Styrene (ABS) – ABS is a high-strength, high-temperature-resistant plastic that comes in multiple colors, which makes it ideal for end-use parts, such as DIN rails.
- Acetyl ESD – Acetyl, or polyoxymethylene (POM), is preferred for its inherent static dissipative properties. It contains no carbon fibers and has 109-1011 ohm/square surface resistivity.
Plastic Fabrication in the Aerospace Industry
 Weight reduction and durability are the primary reasons plastics have become common in aerospace applications. Many plastics are resistant to corrosion, extreme temperatures, flame, vibration, and wear. This makes them an obvious choice for high-risk aeronautics. Also, since CNC plastic fabrication allows for easy prototyping, it’s an ideal choice for new product introductions in this high-risk industry.
Weight reduction and durability are the primary reasons plastics have become common in aerospace applications. Many plastics are resistant to corrosion, extreme temperatures, flame, vibration, and wear. This makes them an obvious choice for high-risk aeronautics. Also, since CNC plastic fabrication allows for easy prototyping, it’s an ideal choice for new product introductions in this high-risk industry.
Popular materials used in aerospace applications include:
- PTFE/Teflon® – Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly referred to by the trade name Teflon®, is preferred for its inflammability, low dielectric properties, and high-temperature resistance. PTFE is used for fuel system parts, electric harnesses, and insulators.
- ULTEM® – ULTEM is a polyetherimide (PEI) material that resists stress cracking and is inherently flame resistant. This plastic retains its strength and stiffness at temperatures up to 392 degrees F.
- Duratron® PAI – PAI, or polyamide-imide, maintains its strength and stiffness at continuous temperatures up to 500 degrees F. PAI is used for aircraft bearings, electrical connectors, and mandrels.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), referenced above as ideal for medical devices, is commonly found in aerospace parts as well.
As you can see, each of these industries has its unique requirements for the type of plastic material used. It’s important to work with a qualified supplier who understands the intricacies of custom plastic fabrication and the specific needs of your industry.
At HP Manufacturing, we have more than 80 years of experience in machining and assembling plastics. Our detailed feedback and engineering analyses of even the most intricate designs ensure the final product performs beyond expectations. We partner with our customers and are honored by their trust in our expertise. We believe in striking a balance between product quality and cost to deliver the very best value to the customer.
Contact an Applications Specialist for help designing your custom plastic fabrication.
Any OEM looking for custom, quality plastic components manufactured to tight tolerances inevitably looks to CNC machining. It not only offers the quality needed, but its fast start-up time (no molds are required) makes it the go-to choice for many design engineers.
Because plastic fabrication is used in a variety of industries, including industrial and heavy equipment, medical, electronics and aerospace, engineers need to understand the materials and special requirements most commonly seen in each sector to make informed design decisions to best leverage plastic fabrication technology for their projects.
Plastic Fabrication in Industrial Applications
 CNC machining offers the widest variety of materials options, which makes it the premier choice for industrial applications. Machinery and heavy equipment manufacturers use plastics for a diverse range of components, including wear pads, protective guarding, gears, housings, valves, spacers, cable management, and more. These parts often require high-stress, high-load, high-temperature, or chemical resistance.
CNC machining offers the widest variety of materials options, which makes it the premier choice for industrial applications. Machinery and heavy equipment manufacturers use plastics for a diverse range of components, including wear pads, protective guarding, gears, housings, valves, spacers, cable management, and more. These parts often require high-stress, high-load, high-temperature, or chemical resistance.
Some of the most popular materials for industrial plastic fabrication include:
- Polycarbonate (PC) – PC is a durable plastic that can withstand environments and high temperatures. Polycarbonate has great clarity.
- Nylons – These polyamide materials are among the most common plastics used in industrial applications due to their strength and durability. Nylon is a relatively inexpensive material that is easily machined to extremely tight tolerances.
- Delrin® – This acetal homopolymer is often used to replace metal due to its density, stiffness, and tensile strength. This impact-resistant material is ideal for applications where the part is moving or exposed to moisture and chemicals.
- TIVAR® 88 – TIVAR polyethylene is ideal for applications requiring corrosion, moisture, and wear resistance at temperatures up to 175 degrees F.
- UHMW – Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene features excellent abrasion and impact resistance, as well as noise reduction. Being chemically inert, UHMW is ideal for industrial food contact applications.
Plastic Fabrication in the Medical Industry
Plastics have become an integral part of the healthcare industry for everything from single-use disposables to implants to the equipment used to diagnose illnesses. OEMs of Class II and III medical devices face strict regulatory requirements in the design and manufacture of their products. The components used in these devices may require the plastic to be safe for human contact, antimicrobial, compatible with repeated sterilization, and able to support complex geometries.
One of the most important factors for fabricated medical plastics is ensuring your supplier can machine and assemble these devices with extremely tight tolerances and repeatable quality. Fabricators also need to provide you with certified materials, serialization, BOM management, full traceability, and Certificates of Conformance. REACH and RoHS compliance may also be required.
Materials commonly used in medical fabrications include:
- Acrylic/Plexiglas® – Scientifically known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), acrylic is favored for its crystal clarity, shatter resistance, light weight, cleanability, and machinability. PMMA is used in diagnostic imaging phantoms, in fluoroscopic pediatric cradles, and in other immobilization braces used in medical imaging.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) – PEEK is ideal for medical devices due to its mechanical strength and elasticity. PEEK also is resilient to radiation, high temperatures, abrasion, and wear.
- Polycarbonate (PC) – One of the most versatile plastics for fabrication, polycarbonate material is autoclavable, impact-resistant, and offers superior clarity for medical applications. PC can be found in surgical instruments, connectors, centrifuge bowls, and more.
Custom Fabrication for Electrical and Electronic Devices
Plastics are the go-to choice for electronic components due to their non-conductive, static-dissipative, and nonflammable options. Many plastics can withstand high voltages and temperatures without material degradation, and their corrosion- and water-resistance increase product safety and reliability. Plus, the machinability of plastics enables virtually unlimited options in complex electrical designs.
Materials often used in electrical and electronic assemblies include:
- GPO-3 – This glass-reinforced polyester is a durable, impact-resistant plastic with outstanding flame, arc, and track resistance. GPO-3 is used to make electrical insulators, terminal blocks, and strain reliefs.
- Acrylonite Butadiene Styrene (ABS) – ABS is a high-strength, high-temperature-resistant plastic that comes in multiple colors, which makes it ideal for end-use parts, such as DIN rails.
- Acetyl ESD – Acetyl, or polyoxymethylene (POM), is preferred for its inherent static dissipative properties. It contains no carbon fibers and has 109-1011 ohm/square surface resistivity.
Plastic Fabrication in the Aerospace Industry
 Weight reduction and durability are the primary reasons plastics have become common in aerospace applications. Many plastics are resistant to corrosion, extreme temperatures, flame, vibration, and wear. This makes them an obvious choice for high-risk aeronautics. Also, since CNC plastic fabrication allows for easy prototyping, it’s an ideal choice for new product introductions in this high-risk industry.
Weight reduction and durability are the primary reasons plastics have become common in aerospace applications. Many plastics are resistant to corrosion, extreme temperatures, flame, vibration, and wear. This makes them an obvious choice for high-risk aeronautics. Also, since CNC plastic fabrication allows for easy prototyping, it’s an ideal choice for new product introductions in this high-risk industry.
Popular materials used in aerospace applications include:
- PTFE/Teflon® – Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly referred to by the trade name Teflon®, is preferred for its inflammability, low dielectric properties, and high-temperature resistance. PTFE is used for fuel system parts, electric harnesses, and insulators.
- ULTEM® – ULTEM is a polyetherimide (PEI) material that resists stress cracking and is inherently flame resistant. This plastic retains its strength and stiffness at temperatures up to 392 degrees F.
- Duratron® PAI – PAI, or polyamide-imide, maintains its strength and stiffness at continuous temperatures up to 500 degrees F. PAI is used for aircraft bearings, electrical connectors, and mandrels.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), referenced above as ideal for medical devices, is commonly found in aerospace parts as well.
As you can see, each of these industries has its unique requirements for the type of plastic material used. It’s important to work with a qualified supplier who understands the intricacies of custom plastic fabrication and the specific needs of your industry.
At HP Manufacturing, we have more than 80 years of experience in machining and assembling plastics. Our detailed feedback and engineering analyses of even the most intricate designs ensure the final product performs beyond expectations. We partner with our customers and are honored by their trust in our expertise. We believe in striking a balance between product quality and cost to deliver the very best value to the customer.
Contact an Applications Specialist for help designing your custom plastic fabrication.