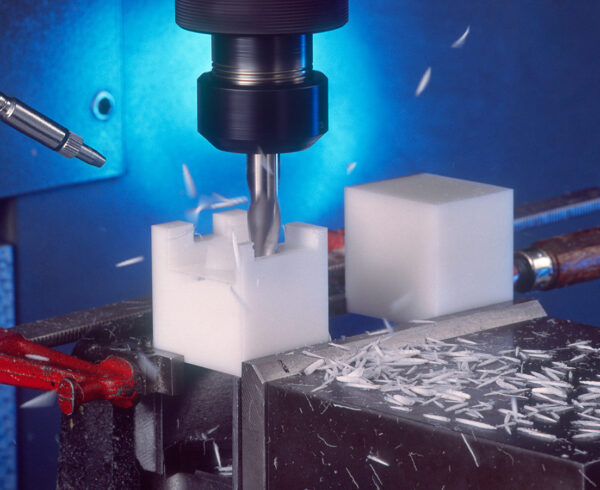
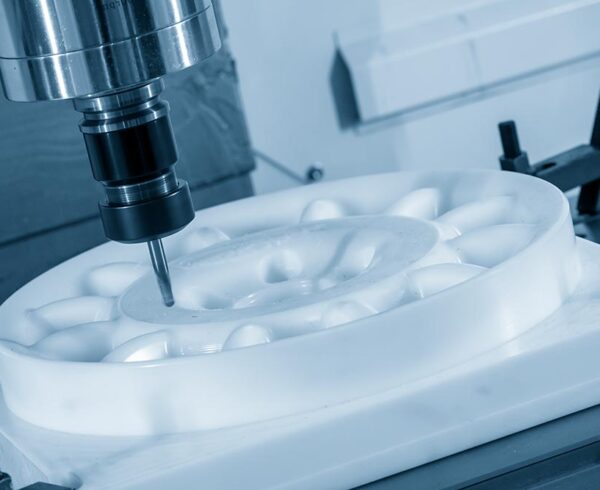
Acetal, also known as polyoxymethylene (POM), offers excellent mechanical properties, but it also presents some challenges during the machining process. Plastic fabricators who work with acetal require a high level of machining expertise due to the material’s unique properties and characteristics.
Types of Acetal
Regarding the types of acetal available, there are two primary types:
Homopolymer acetal: This type of acetal is made solely from the polymerization of formaldehyde. It offers high strength, stiffness and dimensional stability, making it suitable for applications such as gears, bearings, pump components and automotive parts.
Copolymer acetal: Copolymer acetal is a blend of formaldehyde homopolymers and ethylene oxide. It possesses similar mechanical properties to homopolymer acetal but has improved thermal stability and chemical resistance. Copolymer acetal is commonly used in automotive, electrical and consumer goods industries.
Benefits of Acetal
Acetal is a versatile engineering thermoplastic that offers several benefits in various applications. Some of the benefits of parts made with acetal include:
- Excellent mechanical properties: Acetal has high tensile strength, stiffness and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications that require strong and durable components. Because of this, acetal is widely used for components like strain reliefs, gears and positioning devices in the medical diagnostic imaging equipment industry.
- Low friction and wear resistance: Acetal exhibits low friction characteristics, which makes it an ideal choice for applications involving sliding or rotating parts. It also has excellent wear resistance, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement.
- Dimensional stability: Acetal has good dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size even in high-temperature or high-moisture environments. This property is crucial for parts that require tight tolerances or need to function accurately over time.
- Chemical resistance: Acetal is resistant to many chemicals, including solvents, fuels and various oils. This property allows it to be used in applications where exposure to chemicals is expected.
- Electrical insulating properties: Acetal is an excellent electrical insulator, making it suitable for electrical and electronic applications where insulation is critical.
Challenges of Acetal
While acetal offers several benefits, there are also some properties and challenges to consider when selecting it for a component:
- Limited resistance to strong acids and bases: While acetal exhibits good chemical resistance, it may not withstand prolonged exposure to strong acids or bases. In such cases, alternative materials may be more suitable. You can find technical specs on other engineering/mechanical plastics here.
- Susceptibility to degradation under UV exposure: Acetal can degrade when exposed to prolonged UV radiation, which can cause discoloration, reduced mechanical properties and surface cracking. You might need to add UV stabilization or appropriate coatings for outdoor or UV-exposed applications.
- Low resistance to certain solvents: Acetal is generally resistant to many common solvents, but it can be affected by some strong polar solvents, such as ketones. Compatibility with specific chemicals should be evaluated for each application.
- >Water absorption: Acetal can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment, which may affect its dimensional stability and mechanical properties. This moisture absorption should be considered in applications where dimensional accuracy is critical.
What to Ask When Choosing a Plastics Machining Partner for Your Acetal Component
One crucial aspect of machining acetal is understanding its thermal properties. Acetal has a relatively high melting point and requires higher processing temperatures compared to some other thermoplastics. Ask if the machinists making your component are knowledgeable about the appropriate cutting speeds, feed rates and tool materials that can withstand these elevated temperatures. Additionally, they need to understand the heat dissipation characteristics of acetal is important to prevent overheating and potential damage to the workpiece or the cutting tools.
Another consideration when machining acetal is its low thermal conductivity. Acetal has poor heat dissipation properties, which means that heat generated during the machining process tends to concentrate in the tool and the workpiece. This can lead to issues such as tool wear, melting or burning of the material, and dimensional inaccuracies. Do the machinists have expertise in optimizing machining parameters, selecting suitable cooling techniques and using appropriate tool geometries to manage heat effectively and maintain dimensional stability?
Furthermore, acetal tends to produce long, stringy chips during machining. These chips can cause problems such as tool clogging, surface finish issues, or poor chip evacuation if not managed properly. Machinists need to be skilled in chip control techniques, such as using appropriate cutting tool geometries, chip breakers and coolant strategies to ensure smooth chip formation and removal.
Additionally, as acetal can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment, it is essential to store the material properly and ensure it is adequately dried before machining. Moisture content can affect the material’s properties, including dimensional stability and surface finish. Find out if the machinists take the necessary precautions and use appropriate techniques for handling and machining acetal in moisture-sensitive applications.
Working confidently with acetal requires machining expertise that encompasses knowledge of its thermal properties, heat dissipation management, chip control and moisture sensitivity. Machinists with experience in working with acetal can optimize machining parameters, select appropriate tools and implement effective cooling and chip control strategies to achieve accurate, high-quality parts while minimizing issues such as tool wear, material deformation or poor surface finish.
Finding the Right Partner for Your Acetal Components
Overall, acetal is a valuable engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance and dimensional stability. It finds applications in a wide range of industries, including automotive, electrical, consumer goods and more.
At HP Manufacturing, our experienced machinists produce high-quality parts from a wide range of acetal plastics. Ask us about your next plastic fabrication project using acetal or another specialty material. We deliver on time and within budget.